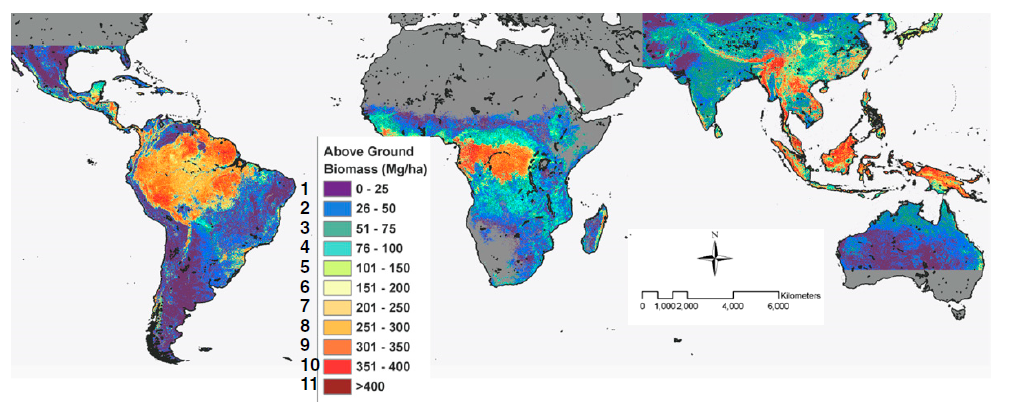
Following on from the last few blog posts, a third technique for estimating aboveground carbon stocks is through remote sensing. Remote sensing has relevance for my project since we are using it to identify cocoa farm typologies at a large (national) scale and I will indirectly use it to classify the carbon stock of those typologies.
Remote sensing and satellite imagery techniques can cover large ages and can be used for landscape classification when combined with secondary spatial information. Broad forest types at the landscape level and even tree dimensions at the plot level can be estimated which can then be converted into biomass using statistical relationships (Brown, 1997; Chave et al., 2005; Saatchi et al., 2011). Remote sensing techniques can broadly be grouped into categories of optical sensing, high-resolution satellite imagery, microwave or radar, and LiDAR. Continue reading “Estimating aboveground carbon stock in forests: Remote sensing”