Scaling legumes entrepreneurship is a big deal!! Here is why;
Legume-based entrepreneurship is very essential in developing countries including my research focus countries, for varied reasons. Most importantly, previous research shows that it creates supply and demand conditions that drive nature positive food production systems that meet human food security, nutrition, social and economic needs.
Legumes provide vast benefits to mankind. Below are some benefits of legumes
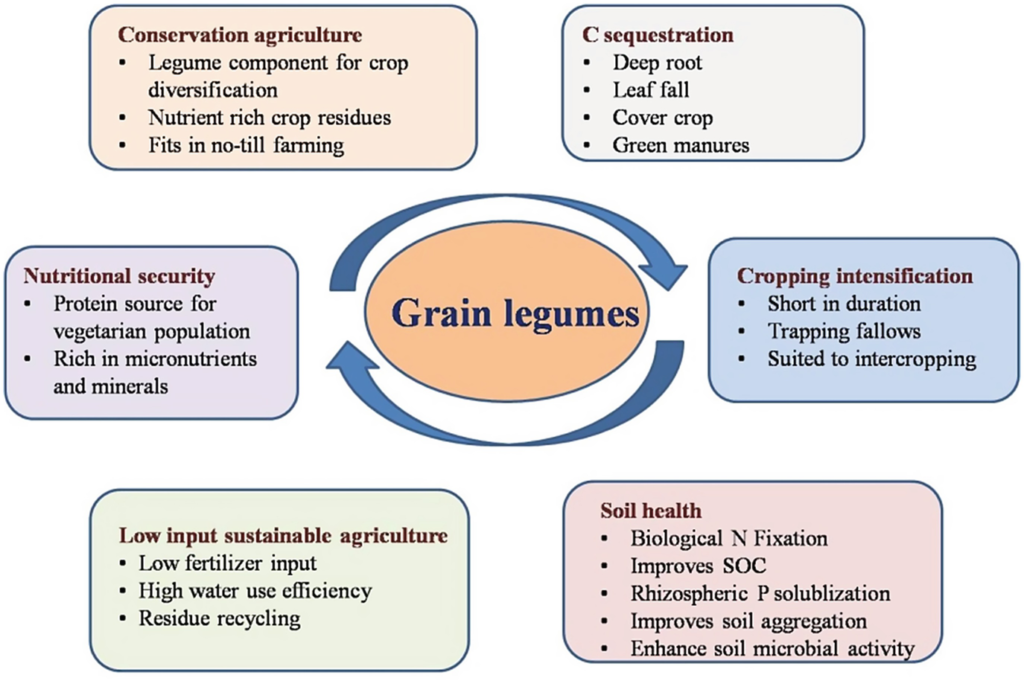
As one can see from the figure above, previous research has shown that legumes promote agroecological principles, improves soil health and fertility, and they are climate-smart in both reducing indirect greenhouse gas emissions associated with fertilisers, and build builds climate change and drought resilience. Moreover, their role in providing a rich, affordable protein source that improves the health of the poor (nutrition and food security) cannot be over-emphasised. Their role also in providing opportunities for gender-responsive rural economies diversification, legume-based enterprises establishment, trade, and exports has been adequately documented in the literature. This surely addresses many sustainable development goals, including ending hunger, good health and wellbeing, gender equality, and climate action among others.
Scaling legumes entrepreneurship enhances all these benefits and Yes it can make a big difference! As past research has shown that, entrepreneurship spurs innovation, this enhances opportunities for increased income and employment for rural youth and women, and economic development. Schumpeter and Backhaus (2003) have long emphasised the role of entrepreneurship which they have centered at the heart of economic theory and practice. In the same manner, legumes entrepreneurship is a big deal that increases legumes-based innovation, productivity, and legumes business dynamism. This provides the impetus for scaling legumes, which have low adoption rates in East Africa, and sub-Saharan Africa as a whole.
However, previous research has shown many barriers which include lack of policy support, advisory and extension services, improved varieties, financial capital, improved innovative practices, prices instabilities, poor markets, poor seed support systems millitates against efforts to scale legumes-based entrepreneurship. This means that entrepreneurship scaling will need clear efforts targeting value chain development, capacity building, innovations, partnerships, among others.
In summary, scaling legumes entrepreneurship is a very big deal! which have the potential to meet both environmental, social, and economic goals that enhance the welfare of women, youth, and the poor and contributing to the economic development of the developing countries.
Some Useful References
FARINHA, L., FERREIRA, J. J. M. & NUNES, S. 2018. Linking innovation and entrepreneurship to economic growth. Competitiveness Review: An International Business Journal, 28, 451-475.
MAWOIS, M., VIDAL, A., REVOYRON, E., CASAGRANDE, M., JEUFFROY, M.-H. & LE BAIL, M. 2019. Transition to legume-based farming systems requires stable outlets, learning, and peer-networking. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 39, 14
OJIEWO, C., RUBYOGO, J. C., WESONGA, J., BISHAW, Z., ABANG, M. M. & GELALCHA, S. 2018. Mainstreaming efficient legume seed systems in Eastern Africa: challenges, opportunities and contributions towards improved livelihoods, FAO.
Schumpeter J., Backhaus U. (2003) The Theory of Economic Development. In: Backhaus J. (eds) Joseph Alois Schumpeter. The European Heritage in Economics and the Social Sciences, vol 1. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-48082-4_3
TESFAI, M., NJARUI, D. & GHIMIRE, S. R. 2019. Sustainable intensifications of African agriculture through legume-based cropping and Brachiaria forage systems. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 14, 1138-1148.