Grey Water Footprint- What Pollutants are in Agricultural Water?
The grey water footprint represents the amount of water required to dilute pollutants so that the quality of ambient water remains above agreed water quality standards (Hoekstra et al., 2009). For coffee production, this would be the volume of water to dilute levels of nitrate and phosphate (fertilizer) and pesticide levels leaching from soil to ambient standards. These ambient water quality standards are defined as the maximum allowable amount of a polluting substance present in rivers, lakes or groundwater, given as a concentration (WFN, 2008). The table below displays the major water pollutants in agriculture, which shows nutrients, pesticides, salts and sediment to be the main pollutants in crop production systems.
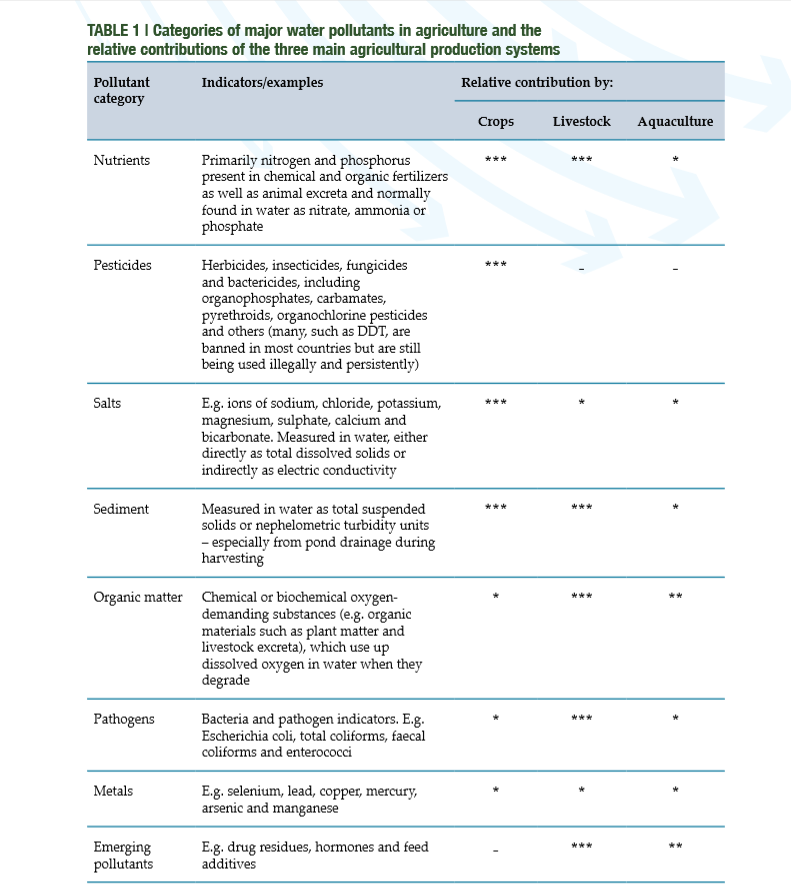
FAO (2017). Water pollution from agriculture: a global review. Executive summary.
Ene & Teodosiu (2011). Grey Water Footprint Assessment and Challenges for its Implementation. Environmental engineering and management journal. 10(3), 333-340.