Research Progress within the Past Week
This week, as I delved deeper into the fascinating domain of sustainable agriculture, I investigated the potential of feed additives to reduce methane emissions from enteric fermentation. I embarked on a search for answers with the objective of reducing environmental impact while enhancing animal welfare.
Research Goal/Objectives
The study sought to assess and quantify the benefits of feed additives in ruminant livestock from an environmental assessment perspective, with the primary objectives of determining the efficacy of feed additives in reducing methane emissions, evaluating their impact on animal health and welfare, and contributing to the body of knowledge in sustainable livestock production.
What Was Done?
Throughout the course of this week, I examined a vast array of scientific literature pertaining to the effects of various feed additives on ruminant livestock methane emissions. I also analyzed the mechanisms by which these additives function, including inhibition of methanogenesis and rumen environment modification.
What Was Achieved?
The comprehensive review facilitated a deeper comprehension of the potential of feed additives to reduce methane emissions. Key additives, such as three-nitroxypropanol (3NOP), nitrates, and halogenated compounds found in macroalgae, have demonstrated promising results in inhibiting methanogenic archaea and reducing methane production.
Headline Research Findings
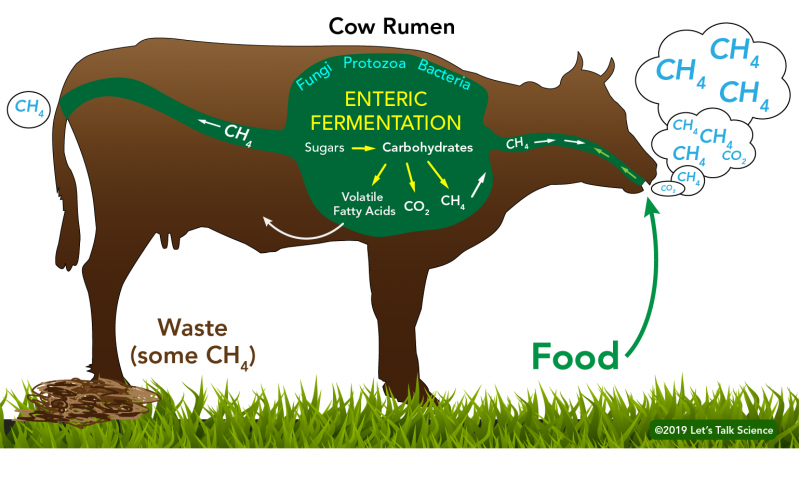
Through investigation, it was discovered that feed additives, especially 3NOP, halogenated CH4 analogs, and nitrates, have exhibited significant potential in preventing methanogenesis. These additives reduce methane emissions from ruminant livestock by either directly inhibiting methanogens or competing with them for substrates.

Reflections on What I Learned This Week
Understanding the intricate interplay between feed additives, methane emissions, and livestock health was crucial to this week’s work. The importance of contemplating not only environmental impacts but also animal welfare in sustainable agricultural practices was discovered. In addition, working collaboratively with the respective supervisors enabled fruitful discussions and the exchange of insights, which enriched the research experience.
Research Plans for Next Week
The upcoming week will have a dual emphasis that will gradually increase. The first objective will be to dig a bit deeper into the specific mechanisms by which feed additives inhibit methanogenesis in order to gain a more nuanced comprehension of their effects on rumen microbial populations. Second, the objective is to investigate the potential synergies between various feed additives and their combined effects on methane reduction, with the goal of achieving a holistic approach to enhancing sustainability and animal welfare.
The unraveling of the cutting-edge approaches feed additives provide in the pursuit of sustainable livestock production and a greener future will be revealed next week, so stay tuned.
Disclaimer: The information presented in this blog post is based on the research progress made within the past week and is subject to further exploration and validation.